Seasonality of Subprime Lender Transactions
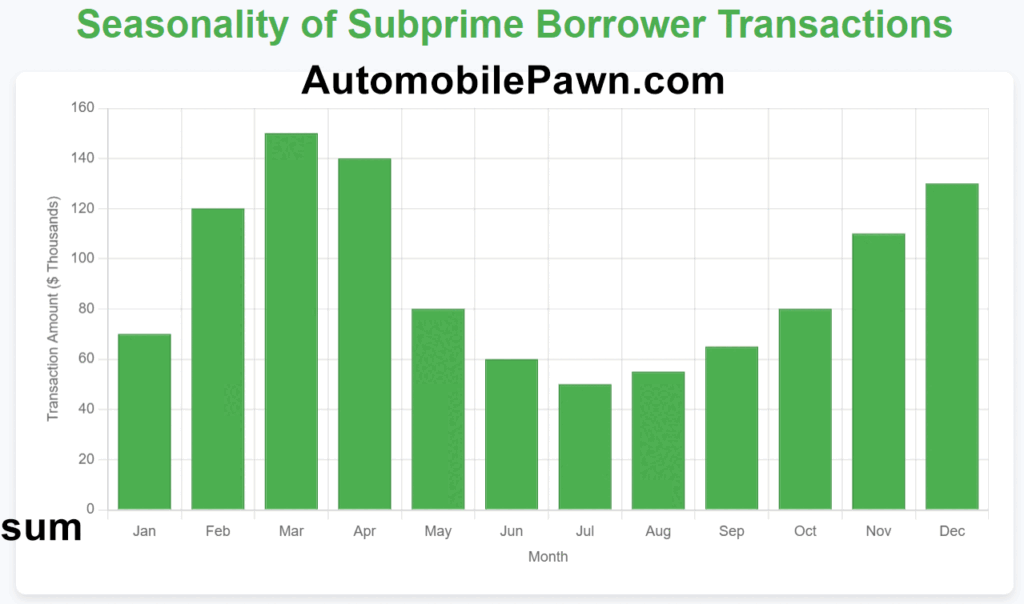
Timing is everything in lending, especially when serving credit-challenged borrowers.
Understanding the rhythms of demand—when needs spike and when they settle, can mean the difference between missed opportunities and maximized profits.
The table below captures the seasonality of subprime borrower transactions, revealing the patterns that drive their financial behavior.
Armed with these insights, subprime lenders can anticipate demand, tailor their offerings, and stay one step ahead in meeting the needs of their customers at just the right moment.
Trans Union Data

Every great business decision starts with clarity.
In the world of subprime lending, where challenges and opportunities collide, understanding the landscape is the key to thriving.
The table below distills essential insights and actionable strategies, offering a clear path for lenders who serve credit-challenged consumers.
Whether navigating rising delinquencies, regulatory constraints, or shifting borrower behavior, this analysis equips you with the tools to turn obstacles into opportunities and ensure profitability in a competitive market.
Subprime Lending: Insights and Strategies for Profitable Growth
| Category | Observations/Analysis | Strategies for Subprime Lenders |
|---|---|---|
| Delinquency Trends | 60+ DPDs increased for UPLs for the 4th consecutive month. Bankcard 90+ DPDs are flat, but balances increased (+0.6% MoM). | Implement real-time borrower analytics to detect early warning signs of default. Adjust underwriting criteria seasonally. |
| Loan Origination | Subprime originations fell across multiple channels: fintechs (-11.6% MoM), credit unions (-22.1% MoM). Finance companies saw YoY increases in subprime originations (+34.3%). | Diversify portfolio with loan products targeting near-prime borrowers. Target secured loans like auto title loans to mitigate risks. |
| Market Share | Finance companies lead UPL balances (29%), followed by fintechs (27.8%). Subprime borrowers are migrating toward nontraditional lenders. | Leverage digital platforms to improve accessibility and capture underserved demographics. Offer mobile-first experiences for onboarding. |
| Rising Borrower Stress | Subprime delinquencies rising due to inflation, high cost of living, and increased bankcard balances. Borrowers prioritize secured debts. | Provide financial literacy resources to educate borrowers. Introduce loan consolidation programs. |
| Risk Management | Default risks rising for subprime loans due to macroeconomic pressures. | Use behavioral data alongside credit scores for advanced risk profiling. Automate collections with predictive analytics. |
| Seasonality | Tax season presents high demand for liquidity among subprime consumers. End-of-year obligations drive borrowing needs. | Launch tax refund anticipation loans and targeted campaigns. Offer flexible repayment plans. |
| Regulatory Constraints | APR caps limit profitability, especially in states with 36% caps. Restrictive policies create "loan deserts." | Use compliant models like multi-state licensing or sovereign nation partnerships. Expand online lending in regulated markets. |
| Operational Efficiency | Rising delinquencies increase operational burden. | Adopt off-the-shelf loan management software. Optimize collections processes. |
| Competitive Environment | Lenders shifting focus to prime and near-prime borrowers, increasing competition. | Develop customized offers for near-prime borrowers. Monitor competitors and adjust product pricing. |
Definitions:
- DPDs = Days Past Due
- MoM = Month Over Month
- UPLs = Unsecured Personal Loans
- Inspired by: Cole Gottlieb and Tansunion
Types of Loans Popular Among Credit-Challenged Consumers
| Loan Type | Description | Potential Seasonality |
|---|---|---|
| Personal loans for bad credit | Offered by online lenders specifically for borrowers with low credit scores. | Demand will increase during periods of economic uncertainty or when consumers face unexpected expenses. |
| Family loans | Borrowing from family members or friends. | More prevalent during times of financial hardship, such as job loss or medical emergencies. |
| Buy now, pay later loans | Short-term financing options that allow consumers to make purchases and pay for them in installments. | Most popular during the holiday season and other periods of increased consumer spending. |
| Cash advance apps | Mobile apps that provide small cash advances, often with fewer fees than payday loans. See Dave.com | Demand is consistent throughout the year, with spikes during emergencies or unexpected expenses. |
| Payday loans | Short-term, high-interest loans due on the borrower's next payday, with a loan length of two to four weeks. | Usage increases during periods of financial strain or when consumers have limited access to other credit options. |
| Credit builder loans | Designed to help improve credit scores for those with no or limited credit history. | Demand is steady throughout the year, as consumers seek to establish or rebuild their credit. |
| Debt consolidation loans | Used to combine multiple debts into one loan with a potentially lower interest rate. | Demand increases during tax refund season or when consumers experience a change in financial circumstances. |
| Car title loans | A type of secured loan where borrowers use their vehicle title as collateral. See AutomobilePawn.com | Demand is higher during periods of economic hardship or when consumers need quick access to cash. |
| Installment loans | Loans that are repaid over a set period of time with fixed payments. | Demand influenced by factors such as interest rates, loan terms, and consumer confidence. |
Subprime Lending Analysis and Strategies
Key Takeaways from the Data:
Subprime Consumer Statistics and Impact:
- Over 50% of U.S. households live paycheck-to-paycheck, and about 40% of households earning $100,000 or more do so.
- Nearly one in three U.S. adults are subprime borrowers (credit scores under 620), with 40% unable to access $400 in an emergency.
- Bankruptcy filings have risen consistently for 19 months, driven by high credit card defaults, inflation, and aggressive debt collection tactics.
- In Illinois, a 36% APR cap resulted in a 44% reduction in loans to subprime borrowers, with consumers turning to illegal or informal sources for credit.
Economic and Policy Context:
- Regulatory measures like the Military Lending Act’s 36% cap have unintentionally created “credit deserts,” where consumers lose access to vital credit products.
- High inflation and increased cost of living have amplified consumer financial stress, increasing demand for small-dollar, short-term loans.
Impact on Subprime Lenders:
- The growing demand for emergency small-dollar loans represents an opportunity for subprime lenders but is constrained by regulatory restrictions, such as APR caps and increasing borrower defaults.
- The seasonality of lending demand, particularly around tax refunds and year-end obligations, presents a critical period for maximizing revenue.
- Stricter regulations reduce profitability by increasing compliance costs and limiting flexibility in pricing loans.
Strategies for Ensuring Profitability for Subprime Lenders:
Regulatory Navigation:
- Employ legal models such as sovereign nation partnerships or multi-state compliance strategies to operate in restrictive environments.
- Maintain a robust compliance framework to preemptively address new legislative challenges.
Diversified Loan Products:
- Offer a range of loans (installment, payday, car title, and lines of credit) to cater to different consumer needs and mitigate revenue impacts from single product restrictions.
- Explore alternative models like installment loans, which spread repayment over time and reduce delinquency rates.
Seasonal Marketing Campaigns:
- Focus marketing efforts during peak periods, such as tax season, when consumer liquidity is strained.
- Provide promotional loan products tied to tax refund advances or holiday financial pressures.
Risk Mitigation and Underwriting:
- Use advanced underwriting tools (e.g., AI-driven scoring, bank account verification) to reduce default risks.
- Implement conservative lending criteria while maintaining accessibility for subprime consumers.
Technology and Digital Channels:
- Develop mobile-friendly lending platforms to capture the growing digital consumer base and streamline loan processes.
- Utilize SMS, email, and social media marketing for higher customer engagement and loan application rates.
- Get your GBP – Google Business Profile setup and functional in order to adverstise via Google without concern for the 36% APR caps!
Customer-Centric Approach:
- Focus on treating borrowers with respect and providing financial literacy resources to improve repayment rates and customer loyalty.
- Provide flexible repayment plans to retain borrowers facing temporary financial setbacks.
Cost Efficiency:
- Automate back-office operations and adopt off-the-shelf loan management software to minimize operating costs.
- Optimize collection processes through centralized tools and predictive analytics to maximize recoveries.
Partnerships and Alliances:
- Collaborate with fintech firms to leverage technology and scale operations efficiently.
- Join industry associations to stay updated on legislative developments and gain access to shared resources.
By implementing these strategies, subprime lenders can navigate regulatory challenges and maximize profitability while meeting the needs of credit-challenged consumers.
4-WAYS I CAN HELP YOU!
Grab a copy of our “bible:” Learn More
Embrace GBP: Google Business Profile in order to overcome Google’s 36% APR Cap! Learn more: LocalListingSuccess.com
Brainstorm: Learn More
The Business of Lending: Learn More
Free Bi-Monthly Newsletter: Learn More
Title Loan Lending: AutomobilePawn.com
